How to Create ‘System Restore’ Points in Ubuntu 18.04
Since I moved up all my work stuff into Linux (mostly Ubuntu 18.04) I’ve been exploring more and more on how to perfect my work environment. Last thing we all need is to not have backups in place. Specially if its a work environment. For that we have TimeShift.
Timeshift for Linux is an application that provides functionality similar to the System Restore feature in Windows and the Time Machine tool in Mac OS. Timeshift protects your system by taking incremental snapshots of the file system at regular intervals. These snapshots can be restored at a later date to undo all changes to the system.
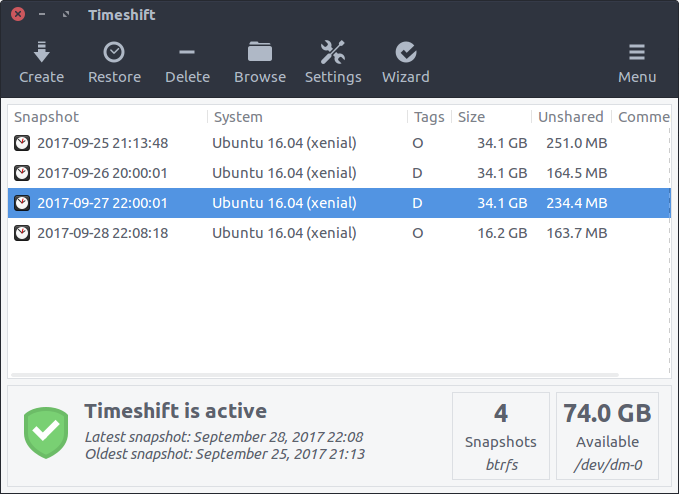
Basically you have two modes:
In RSYNC mode, snapshots are taken using rsync and hard-links. Common files are shared between snapshots which saves disk space. Each snapshot is a full system backup that can be browsed with a file manager.
In BTRFS mode, snapshots are taken using the in-built features of the BTRFS filesystem. BTRFS snapshots are supported only on BTRFS systems having an Ubuntu-type subvolume layout (with @ and @home subvolumes).
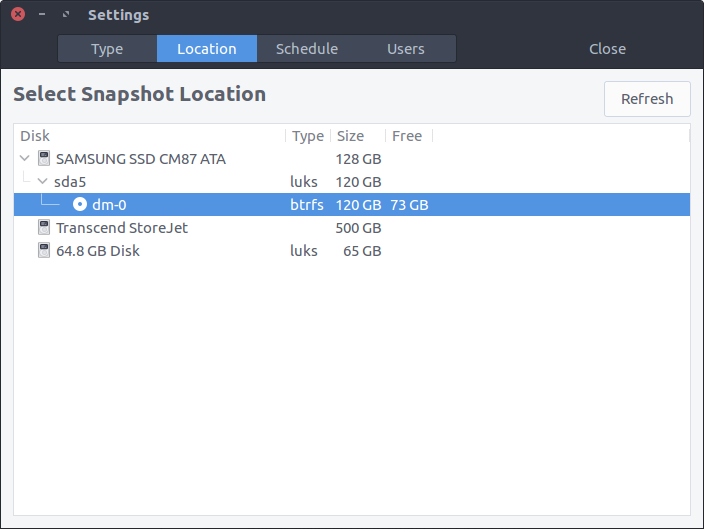
Snapshots are saved by default on the system (root) partition in path /timeshift. Other linux partitions can also be selected. For best results the snapshots should be saved to an external (non-system) partition.
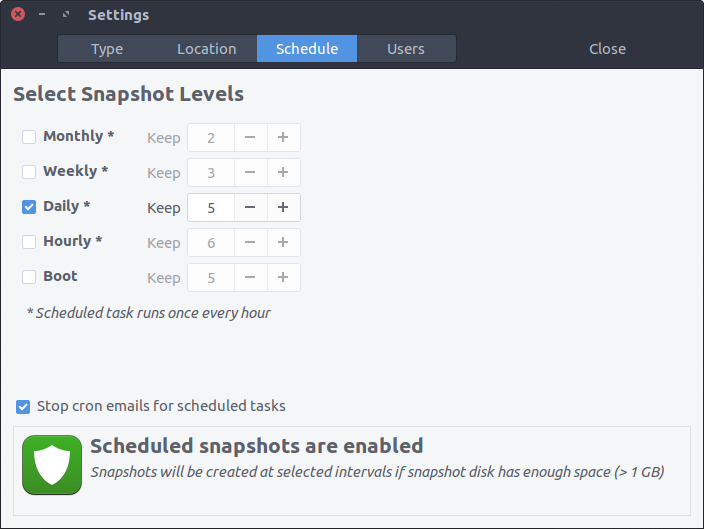
Multiple levels of snapshots can be enabled - Hourly, Daily, Weekly, Monthly and Boot
Installation
Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Elementary OS, etc.
Packages are available in the Launchpad PPA for supported Ubuntu releases. Run the following commands in a terminal window:
$ sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:teejee2008/ppa
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install timeshift
That was easy right? :)